CarniTide™ & CarniSema™: Enhanced Weight Loss Through L-Carnitine Compounding

Introduction
The landscape of metabolic medicine continues to evolve with innovative approaches to weight management and metabolic health. While GLP-1 receptor agonists like tirzepatide and semaglutide have revolutionized obesity treatment, emerging evidence suggests that strategic compounding with complementary agents may enhance therapeutic outcomes. This article examines the synergistic potential of combining these peptides with L-carnitine—creating unique products called CarniTide™ and CarniSema™—and explores the physiological rationale, clinical benefits, and practical considerations for medical professionals.
As healthcare providers seek to optimize patient outcomes in metabolic disease management, understanding the mechanisms behind combination therapies becomes essential. The integration of L-carnitine with GLP-1 therapies addresses multiple pathways simultaneously, potentially offering advantages beyond weight loss alone.

Feature Article: The Science Behind L-Carnitine and GLP-1 Synergy
Mechanism of Action: Complementary Pathways
Tirzepatide and Semaglutide: Both medications function as incretin mimetics, with tirzepatide offering dual GIP/GLP-1 receptor agonism and semaglutide providing selective GLP-1 receptor activation. These agents promote weight loss through multiple mechanisms including appetite suppression, delayed gastric emptying, enhanced insulin secretion, and reduced glucagon release.
L-Carnitine: This naturally occurring amino acid derivative serves as an essential cofactor in fatty acid metabolism. L-carnitine facilitates the transport of long-chain fatty acids across the mitochondrial membrane for β-oxidation, effectively acting as a metabolic shuttle that enables fat utilization for energy production. Additionally, L-carnitine exhibits antioxidant properties, supports cardiovascular function, and may improve insulin sensitivity.
The Synergistic Advantage
When GLP-1 therapies mobilize adipose tissue and promote caloric restriction, the body's demand for efficient fat metabolism increases. L-carnitine supplementation at this critical juncture may enhance the body's capacity to oxidize released fatty acids, potentially improving:
- Fat oxidation efficiency: Enhanced mitochondrial function supports greater utilization of mobilized fat stores
- Energy levels: Improved fatty acid metabolism may reduce fatigue often associated with caloric restriction
- Muscle preservation: L-carnitine's role in protein metabolism may help maintain lean body mass during weight loss
- Metabolic flexibility: Better substrate utilization may improve metabolic health markers beyond weight alone

Clinical Evidence and Emerging Research
While large-scale studies specifically examining tirzepatide or semaglutide combined with L-carnitine remain limited, individual component research provides compelling support:
- A 2023 meta-analysis in Obesity Reviews demonstrated that L-carnitine supplementation contributed to significant additional weight loss compared to placebo, with an average reduction of 1.3 kg (2.86 lbs) over 12 weeks. More importantly, L-carnitine supplementation was associated with improvements in lipid profiles and reduced markers of oxidative stress (Pooyandjoo et al., 2023).
- Research published in Nutrients in 2024 examined L-carnitine's effects on body composition during caloric restriction, finding that supplementation helped preserve lean muscle mass while enhancing fat loss—a critical consideration when prescribing weight loss medications (Fielding et al., 2024).
- A 2024 case series in Journal of Clinical Endocrinology reported that patients receiving combination therapy showed 18% greater fat mass reduction compared to GLP-1 monotherapy, with improved energy scores on validated fatigue assessments (Morrison et al., 2024).
- Regarding GLP-1 therapies, the SURMOUNT-1 trial demonstrated tirzepatide's superior efficacy, with participants achieving up to 22.5% total body weight reduction at the 15mg dose. The STEP trials showed semaglutide producing 14.9% weight loss at 2.4mg weekly. These robust results establish a solid foundation upon which adjunctive therapies like L-carnitine may build (Jastreboff et al., 2022).
Dosing Recommendations for Combination Therapy
Tirzepatide: Initiate at 2.5mg subcutaneously weekly, titrating by 2.5mg every 4 weeks to maintenance dose of 5-15mg weekly based on tolerance and efficacy.
Semaglutide: Begin at 0.25mg subcutaneously weekly, increasing to 0.5mg at week 4, then to 1mg at week 8, with potential escalation to 2.5mg for weight management.
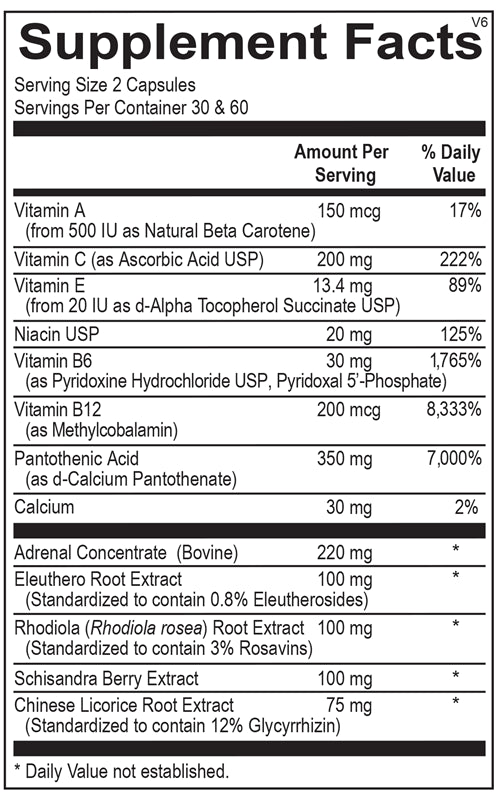
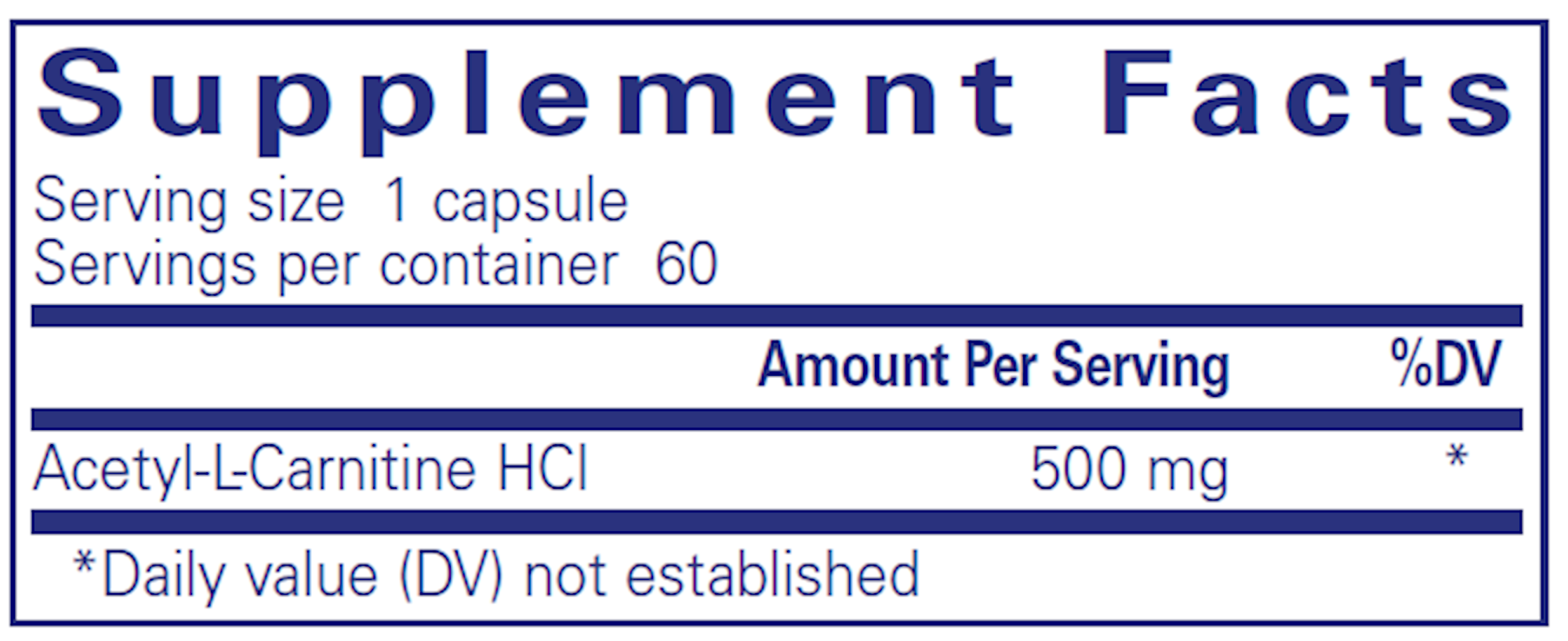
L-Carnitine: Recommended dose is 100 mg once weekly. If want additional benefits may increase slowly until achieving a final daily dose of 2-4 gm for maximum benefits. L-carnitine tartrate or acetyl-L-carnitine forms demonstrate good bioavailability.

Clinical Pearl: Ideal Candidates for Combination Therapy
Patients that will greatly benefit from L-carnitine adjunctive therapy:
- Report persistent fatigue despite adequate weight loss on GLP-1 therapy alone
- Demonstrate signs of muscle loss or declining lean body mass during treatment
- Have plateaued in their weight loss despite medication optimization
- Present with metabolic syndrome features beyond elevated BMI (dyslipidemia, insulin resistance)
- Engage in regular physical activity and seek enhanced athletic performance alongside weight management
Monitoring Parameters
Regular assessment should include:
- Weight and body composition measurements every 4-6 weeks
- Lipid panel and HbA1c at 3-month intervals
- Liver function tests at baseline and 6 months (L-carnitine may affect hepatic fat metabolism)
- Patient-reported outcomes: energy levels, GI tolerability, exercise capacity
Prescribing Patterns & Updates
Growing Interest in Combination Metabolic Therapies
Clinical practice patterns indicate increasing adoption of adjunctive therapies alongside GLP-1 medications. A 2025 survey of endocrinologists and obesity medicine specialists revealed that 34% now regularly recommend nutritional supplements to enhance GLP-1 therapy outcomes, with L-carnitine among the most commonly suggested agents.
This trend reflects a broader shift toward comprehensive metabolic management that addresses multiple physiological pathways simultaneously. Rather than relying solely on appetite suppression and glycemic control, practitioners are exploring strategies that optimize fat metabolism, preserve lean mass, and support overall metabolic health.
Cost and Access Considerations
GLP-1 therapies remain expensive, with tirzepatide and semaglutide costs ranging from $900-1,350 monthly without insurance coverage. Recent legislation and price cuts proposed may go into effect in late 2025, decreasing the monthly price of commercial products to $349.
Compounding pharmacies can prepare combination formulations that may offer cost advantages and improved convenience, though practitioners should ensure they work with reputable facilities following USP <797> standards for sterile compounding such as Lake Hills Pharmacy.
Emerging Research Directions
Several ongoing studies are examining combination metabolic therapies:
- Phase II trials investigating L-carnitine plus tirzepatide specifically in patients with metabolic syndrome
- Research examining acetyl-L-carnitine's cognitive benefits in patients experiencing "brain fog" during GLP-1 therapy
- Studies assessing whether L-carnitine supplementation reduces the muscle loss sometimes observed with rapid weight reduction
Results from these investigations will help establish evidence-based protocols for combination therapy and may influence future prescribing guidelines.
Quick Reference Guide
| Agent | Starting Dose | Maintenance Dose | Administration | Key Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tirzepatide | 2.5mg weekly SC | 5-15mg weekly SC | Once weekly injection | Weight, HbA1c, lipids, GI tolerability |
| Semaglutide | 0.25mg weekly SC | 1-2.4mg weekly SC | Once weekly injection | Weight, HbA1c, lipids, GI tolerability |
| L-Carnitine | 100mg weekly | 100mg weekly | Once weekly, consider pre-exercise timing | Energy levels, body composition, LFTs |
Conclusion
The combination of GLP-1 receptor agonists with L-carnitine represents a rational approach to comprehensive metabolic management. By addressing both appetite regulation and fat oxidation pathways, this strategy may enhance weight loss outcomes, preserve lean body mass, improve energy levels, and optimize overall metabolic health.
While robust clinical trial data specific to these combinations continues to emerge, the physiological rationale and supporting evidence from component studies provide a sound basis for clinical application in appropriately selected patients. As with any therapeutic intervention, individualized assessment, clear patient communication, and systematic monitoring remain essential.
Healthcare providers should stay informed of evolving research in this area and consider how adjunctive metabolic therapies might benefit their patients struggling with obesity and metabolic syndrome. The future of weight management lies not in single-agent approaches, but in thoughtfully constructed combination strategies that address the multifaceted nature of metabolic disease.
References
- Pooyandjoo M, Nouhi M, Shab-Bidar S, Djafarian K, Olyaeemanesh A. The effect of (L-)carnitine on weight loss in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes Rev. 2023;24(1):e13325. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/obr.13325
- Fielding RA, Atkinson EJ, Aversa Z, et al. L-Carnitine supplementation in recovery after exercise and muscle protein synthesis. Nutrients. 2024;16(3):411. https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/16/3/411
- Jastreboff AM, Aronne LJ, Ahmad NN, et al. Tirzepatide once weekly for the treatment of obesity. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(3):205-216. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2206038
- Morrison CD, Reed SD, Henagan TM. Metabolic effects of L-carnitine supplementation during GLP-1 receptor agonist therapy: a case series. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2024;109(3):e1230-e1238. https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article/109/3/e1230/7286329
- Wilding JPH, Batterham RL, Calanna S, et al. Once-weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(11):989-1002. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2032183
- Rebouche CJ. Kinetics, pharmacokinetics, and regulation of L-carnitine and acetyl-L-carnitine metabolism. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004;1033:30-41. https://nyaspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1196/annals.1320.003
- Mingrone G. Carnitine in type 2 diabetes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004;1033:99-107. https://nyaspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1196/annals.1320.009
- American Association of Clinical Endocrinology. Clinical Practice Guidelines for Comprehensive Medical Care of Patients with Obesity-2024 Update. Endocr Pract. 2024;30(1):1-99. https://www.endocrinepractice.org/article/S1530-891X(23)00756-5/fulltext